The application background of Naimo pumps on ships
In the 1960s, offshore oil exploration and development was officially incorporated into China's oil development strategy.
China's oil resources are distributed as follows: 24% offshore and 76% onshore. The offshore oil fields are primarily located in the Bohai Sea, South China Sea, and East China Sea.
The exploitation of offshore oil is primarily conducted by CNOOC
Since the establishment of CNOOC in 1982, the annual production of offshore oil has grown from 90,000 tons to 33.36 million tons of oil equivalent in 2003, both domestically and internationally. In 2008, CNOOC proposed the strategic goal of achieving 40 million cubic meters of oil equivalent domestically, and by 2010, achieving 50 to 55 million cubic meters of oil equivalent domestically, with an additional 20 million cubic meters of oil equivalent from overseas interests. Currently, PetroChina and Sinopec have also joined in the exploration of offshore oil and gas.
Application of Naimo pump in marine mud system
The development of offshore drilling platforms requires more ships to transport cargo and mud
CNOOC Services is a major provider of offshore drilling services in China, with its vessel services accounting for 70% of the Chinese offshore market share. As of March 31, 2007, the company owned 70 various types of workboats, 5 oil tankers, and 4 chemical tankers
Main competitors
Shenzhen Huawei: 20 working vessels
Yantai Rescue and Salvage Bureau of the Ministry of Transport: 10 workboats
Sinopec Group Shanghai Offshore Oil Bureau: 7 workboats
Workboats are used for transporting goods, mud, saltwater, and so on.
The Naimo pump is primarily installed on workboats for the transportation of slurry.
The main purpose and medium condition of Naimo pump
The main purpose of Naimo pump
1. The drilling fluid used for transporting offshore platforms has a specific gravity of about 2.1 and its composition is unknown The price is relatively expensive, about 10000 yuan per ton
2. Transport the seabed mud generated by drilling, mixed with drilled rock debris, containing a small amount of waste mud such as seawater
3. Household waste, wastewater, sludge, etc. generated on the transport ship
Mud Introduction
Also known as drilling fluid, it is the lifeblood of oil wells. In ancient times, the circulating fluid used in drilling was "water", which was used to remove drilling cuttings;
However, with the development of technology today, drilling fluids must possess various other functions in order to complete drilling operations in deep and difficult wells, which we call mud.
There are many functions:
Clearing the wellbore, cooling the drill bit, circulating the crushed rock debris, improving the drilling rate, and forming a mud wall on the inner wall of the wellbore can temporarily protect it from collapse. If barite powder is added to the mud, the specific gravity of the mud can be increased to resist the pressure of the formation, prevent collapse, and prevent formation fluids from invading the wellbore. In case of mud leakage, plugging materials can also be added to the mud to stabilize the wellbore; The viscosity of mud can suspend drilling cuttings, preventing the wellbore from being buried, and has many functions. Therefore, how to achieve a balance point among the various properties of mud and choose the appropriate mud will directly affect the success or failure of drilling projects, which is the biggest challenge for the on-site team leader and mud personnel.
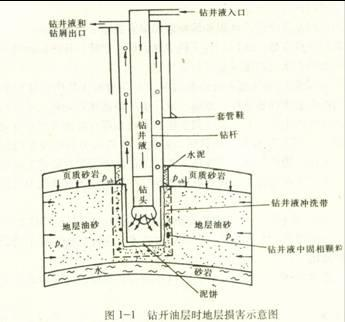
Composition of drilling fluid and mud
The components are complex, such as polymer polyacrylamide, multi ethylene copolymer flocculants, inorganic salts, bentonite slurry, starch, sulfonated phenolic resin products, asphalt products, KCl, viscosity reducers, lime, gypsum, diesel, organic soil, emulsifiers, co emulsifiers, calcium chloride, water, etc., which will not be elaborated here.
Briefly describe the mud system
Ship Mud Handling System, also known as Liquid Mud Handling System, is a new type of cargo handling system. At present, it is mainly used for offshore oil platform supply ships (PSV, AHTS) to provide mud to drilling platforms and oil production platforms, or to recover unused mud on the platform (send it to shore) for processing.
Application of Naimo Pump in Marine Mud System
The system consists of four parts: conveying system - transporting the mud to the platform circulation system - the mud has sedimentation and solidification characteristics, and is kept in circulation during transportation cleaning system - flushing clean for transporting different mud emptying system - emptying the mud in the pipeline through compressed air to prevent condensation and waste.
For Nemo pumps, it means avoiding dry operation For the system, emptying is the most ideal. Therefore, it is necessary to communicate with the system supplier or owner to ensure that the pump does not have a dry running state.
Application of Naimo Pump in Marine Mud System
The schematic diagram of a certain system is as follows:
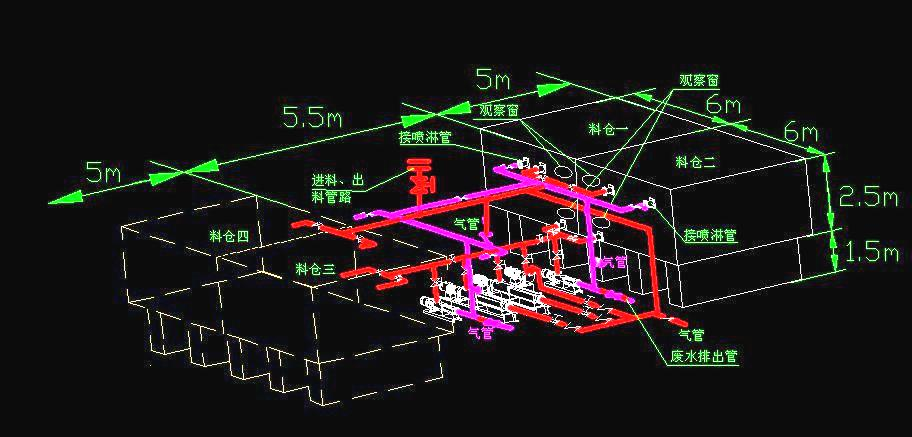
Installation and Selection of Nemo Pump Ship
Installation of Naimo Pump Ship
1. Small in size, occupying minimal space
2. Generally installed in the lower deck room
3. Explosion proof motors are used, which may or may not be required to be explosion-proof;
4. Require classification certification
Naimo pump selection
Shell Material: Cast Iron Shell
Transmission components: 316L
Rotor material: tool steel quenched and wear-resistant
Stator material: SB
Usage time: In practice, the number of times the supply ship transports mud is not very high, and the cumulative pump usage time in a year is not very long. When selecting, it is important to understand the specific working conditions
Naimo pump model
Mud transfer pump NM105SY03S18Z, 75m3/h, 18 bar
Mud circulation pump NM076SY02S12V 22m3/h, 12 bar
Each ship adopts 2 sets of NM105SY03S18V, one for use and one for backup
The number of mud circulation pumps is selected based on the number of silos
Application of Naimo Pump in Marine Mud System

List of major classification societies
Attachment: List of Major Classification Societies
1. Lloyd's Register of Shipping LR
2. French Classification Society BV
3. Italian Classification Society RINA
4. American Bureau of Shipping ABS
5. Det Norske Veritas DNV
6. Germanischer Lloyd GL
7. Japan Maritime Association NK
8. Greek Classification Society HR
9. Russian Ship Registry RS
10. Polish Ship Registry PRS
11. Yugoslav Ship Registry JR
12. Bulgarian Ship Registry BKR
13. China Classification Society (CCS)
14. Czech Ship Registry CSLR
15. Korean Classification Society KR
16. Indonesian Classification Society BKI
17. Romanian Ship Registry RN
18. Indian Classification Society IRS
19. Croatian Ship Registry CRS
Previous :
测试标题名称Next :
为什么选用电动阀门执行器